This topic takes on average 55 minutes to read.
There are a number of interactive features in this resource:
 Biology
Biology
 Chemistry
Chemistry
Cells are building blocks, and there are different parts in different types of cells. Each of these parts, or organelles, has a particular function within the cell, just as each type of cell has a particular function in the body.
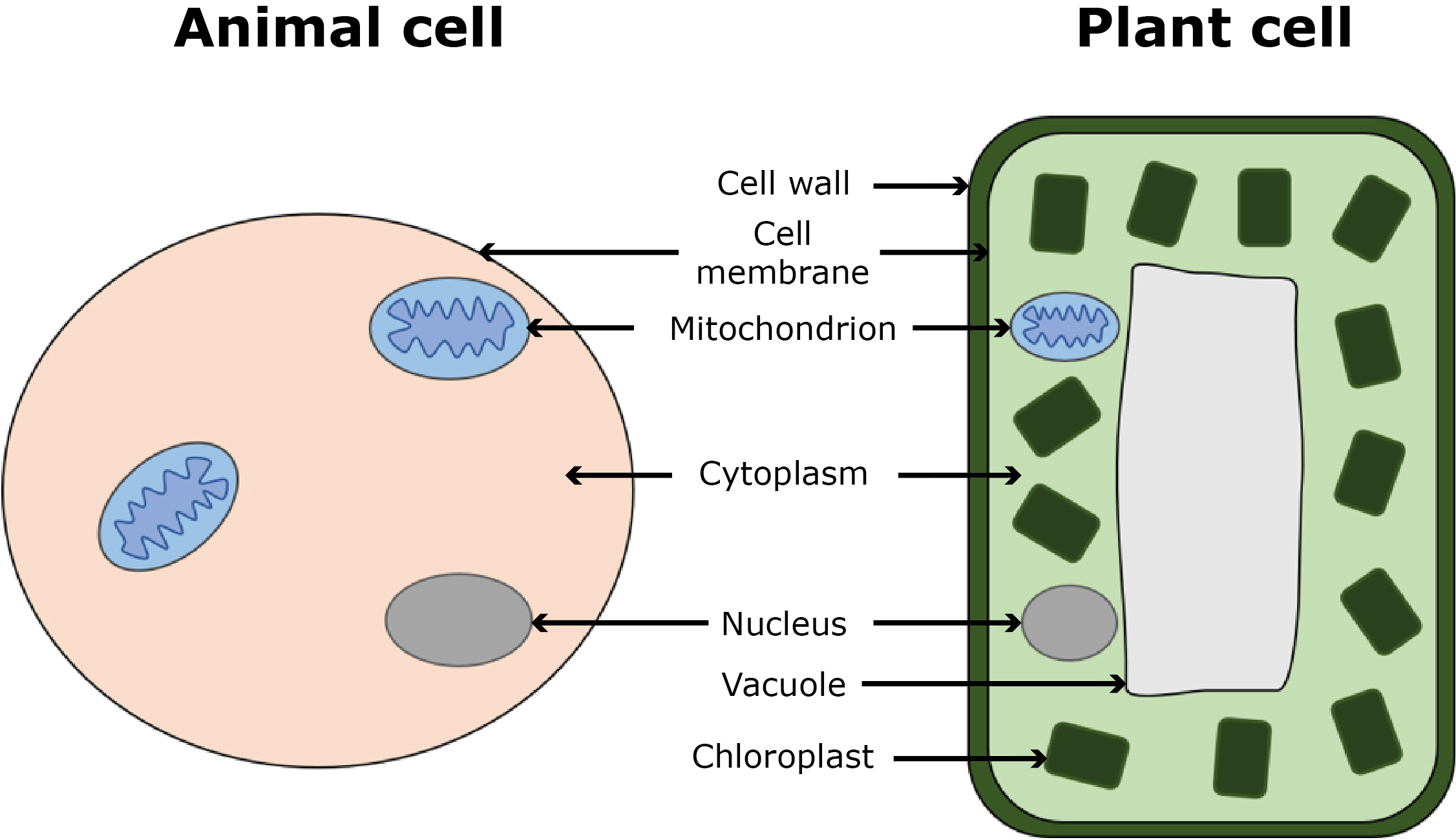
| Organelle | Present in animal cells? | Present in plant cells? | Function |
| Cell membrane | Yes | Yes | The barrier of the cell, regulates what can get in and out of the cell. |
| Cell wall | No | Yes | Gives the cell support and protection. |
| Cytoplasm | Yes | Yes | The inside of the cell, where most cellular reactions occur. |
| Mitochondria | Yes | Yes | The ‘powerhouse of the cell’, where energy for the cell is generated. |
| Nucleus | Yes | Yes | Contains the cell’s genetic blueprint (its DNA). |
| Chloroplast | No | Yes | The location of photosynthesis. |
| Vacuole | No | Yes | Keeps the cell rigid. |
Both animal and plant cells rely on the ability to let certain molecules enter the leave the cell, such as oxygen. They do this through certain processes, such as diffusion. The animation below explains diffusion, osmosis and active transport, which are fundamental to a cell’s survival.