This topic takes on average 55 minutes to read.
There are a number of interactive features in this resource:
 Human biology
Human biology
 Biology
Biology
 PSHE / Citizenship studies
PSHE / Citizenship studies
Glucose is essential for all cells of the body. It provides the 'fuel' for respiration in mitochondria which generates ATP, the energy source for all cell processes. Without a sufficient supply of glucose, cells quickly start to 'shut down' processes. It is therefore important to regulate the supply of glucose in the blood. Brain cells are particularly sensitive to low glucose levels.
Blood glucose levels rise after a meal, as digested food is absorbed in the small intestine, and fall between meals as glucose is used by the cells of the body. The graph shows the fluctuations in glucose levels throughout the day in a person without type 2 diabetes and a person with type 2 diabetes.
If a person with diabetes does not regulate their blood glucose, they can fluctuate between excessively high levels (hyperglycaemia) and too little (hypoglycaemia) glucose. If this situation happens over several years, both can cause problems.
Hyperglycaemia
Hypoglycaemia
These two main hormones are involved in the regulation of blood glucose levels.
Insulin and glucagon regulate blood glucose levels
These two main hormones are involved in the regulation of blood glucose levels.
Insulin and glucagon regulate blood glucose levels. Insulin is produced by the beta cells, whereas glucagon is produced by the alpha cells of the Islets of Langerhans.
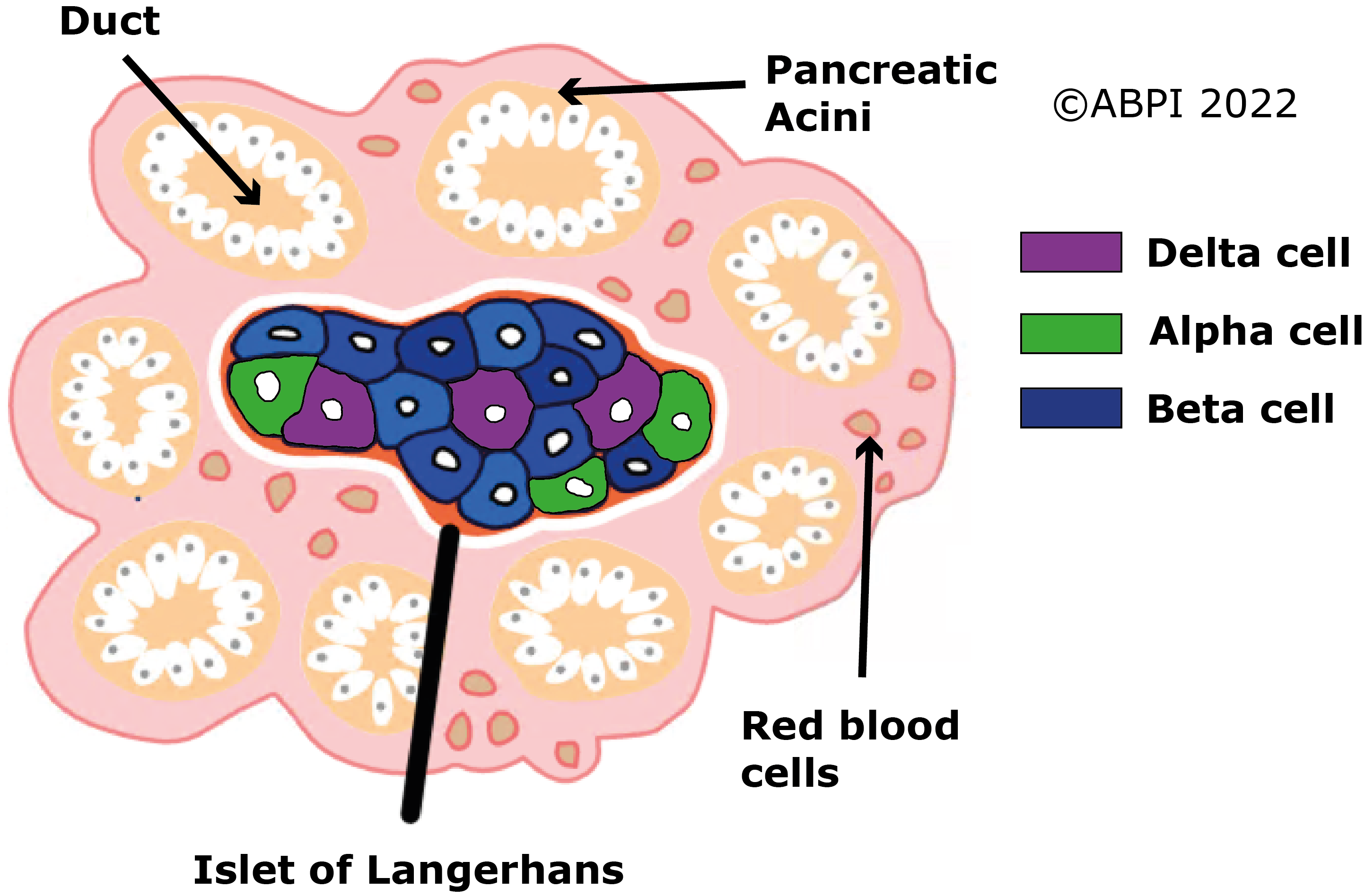
In the animation below, all Islet of Langerhans cells are coloured in blue and no distinction is made between the different types.