This topic takes on average 60 minutes to read.
There are a number of interactive features in this resource:
 Biology
Biology
 Science
Science
Due to climate change, some species are becoming extinct or endangered. This is because the conditions are changing and their homes are either changing or getting destroyed.
If a species becomes extinct, this means that it is removed from the food chain of that habitat.
If a plant or animal is removed from the food chain, this leaves other the plants and animals without any food to eat.
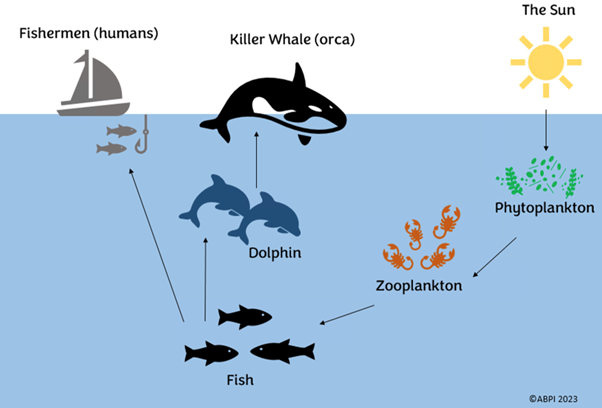
For example, phytoplankton prefer cooler water. The water is heating up because of climate change, meaning that some of the phytoplankton are dying. In fact, there is nearly only half of the phytoplankton that there was 60 years ago.
This means that zooplankton have no food and could die. As fish eat zooplankton, this means that the fish have no food, then the humans, the dolphins, and finally the killer whales.
Being extinct or endangered can also mean that there will be lots of the animal or plant that the removed animal normally eats, as it isn’t being eaten any more. For example, if the dolphins became extinct, there would be lots of fish. This means that the zooplankton food source will become more competitive, and the food chain would be out of balance.
In the sea example, if the fish became extinct, there would be lots of zooplankton. Then, there might not be enough phytoplankton for all of the zooplankton to eat.
This means that climate change is putting food chains at risk. This is why we need to protect our habitats and look after the animals and plants that live in them.
Have a go at labelling this food chain which you might see in a woodland habitat. Decide what the animals are called and whether the animals are a producer or a consumer.
Also have a think about what would happen if the mice became extinct. What would this mean for the caterpillars and the owls?
Remember that the arrows mean energy transfer.
