This topic takes on average 55 minutes to read.
There are a number of interactive features in this resource:
 Biology
Biology
 Human biology
Human biology
 Physical education
Physical education
The outside of your body - your skin - may feel very hot on a sunny summer's day or very cold when it is frosty and snowy. But it is very important that your internal core temperature stays around 37°C whatever the weather and whatever you are doing.
There are three main factors which can affect your core body temperature, sending it up or down.
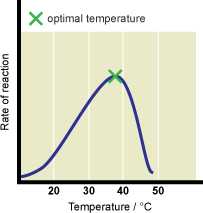
Enzymes are protein molecules which act as biological catalysts, speeding up and controlling all the reactions taking place in the cells of your body. 37°C is the temperature at which these enzymes work best. A few degrees cooler and they work so slowly that the reactions in your cells do not go fast enough to keep you alive. A few degrees higher and the enzymes denature, so they cannot work at all and you will die.
An enzyme is a protein molecule. Each type of enzyme catalyses a particular reaction or type of reaction. They can do this because the long chains of amino acids which make up the enzyme are folded into a particular shape known as the active site. This allows other molecules - the substrates of the reaction - to fit into the enzyme. This works like a lock and key. Once the substrate is in place in the active site it binds to the enzyme and the reaction then takes place rapidly. The products of the reaction are released from the surface of the enzyme.
Enzymes are proteins. If the temperature goes up above about 40°C the long amino acid chains begin to unravel. This changes the shape of the active site. The substrate no longer fits and binds to the active site so the enzyme can no longer catalyse the reaction.